Lepra Cells Definition
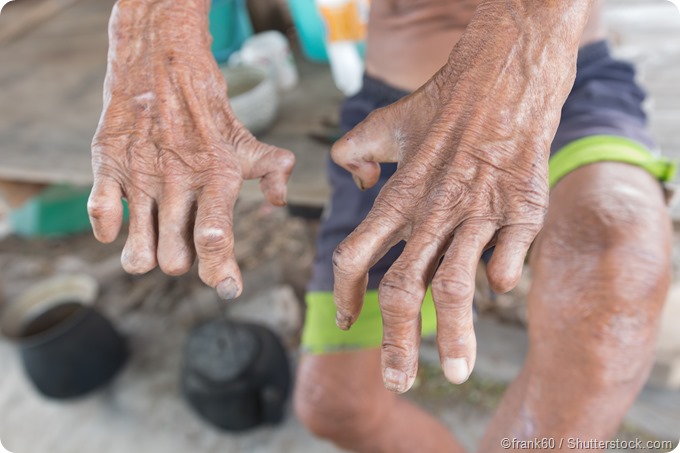
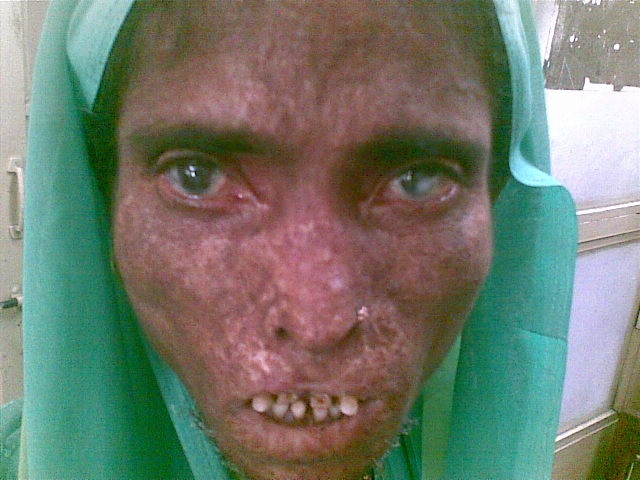
The aetiological agent of leprosy is mycobacterium leprae.
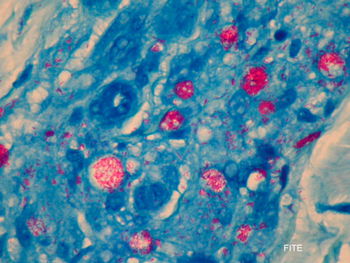
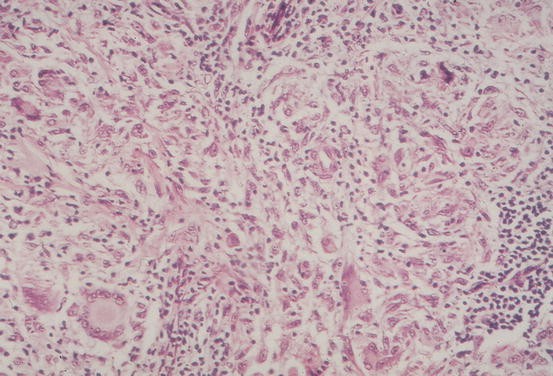
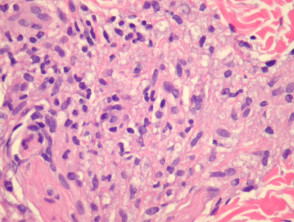
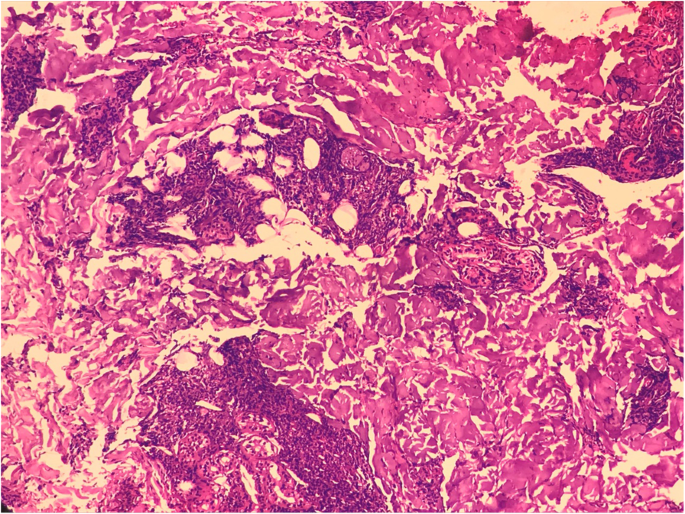
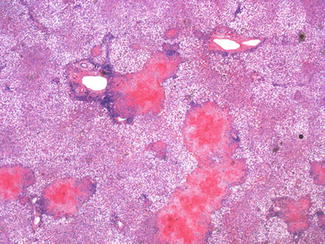
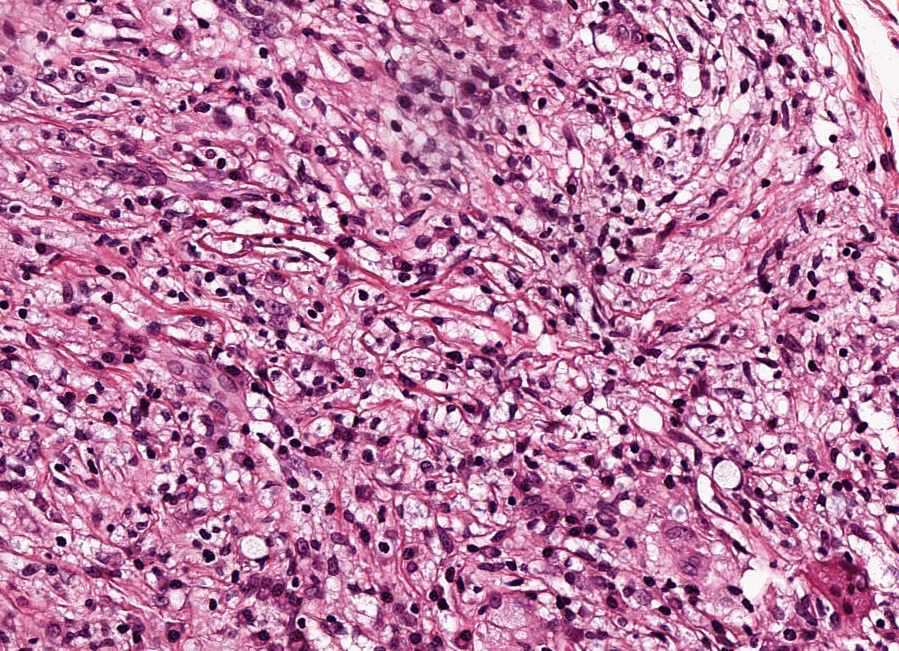
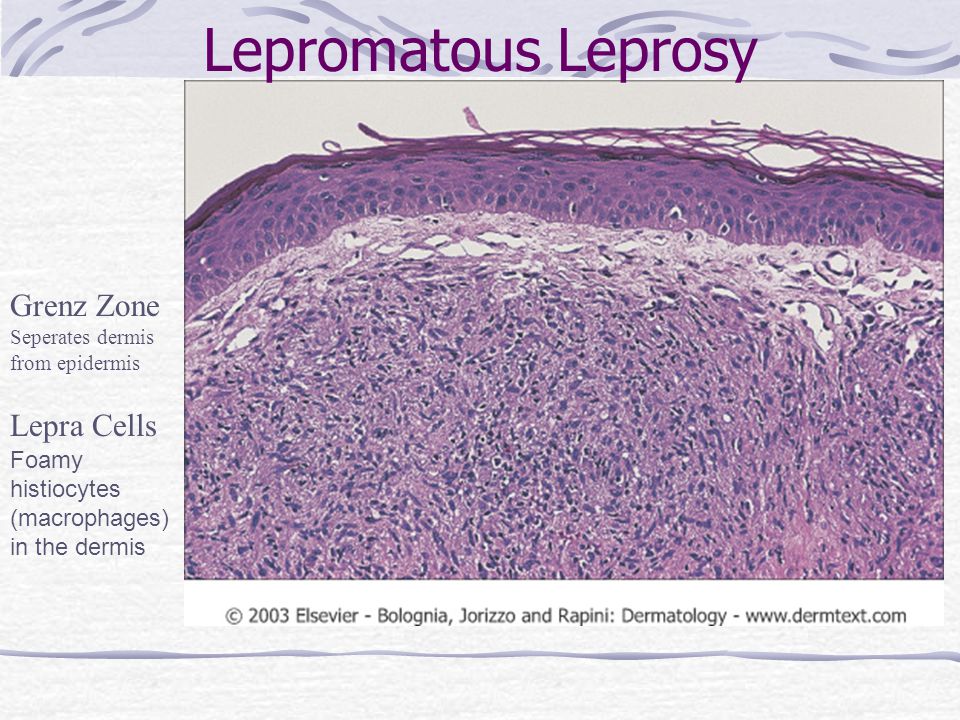
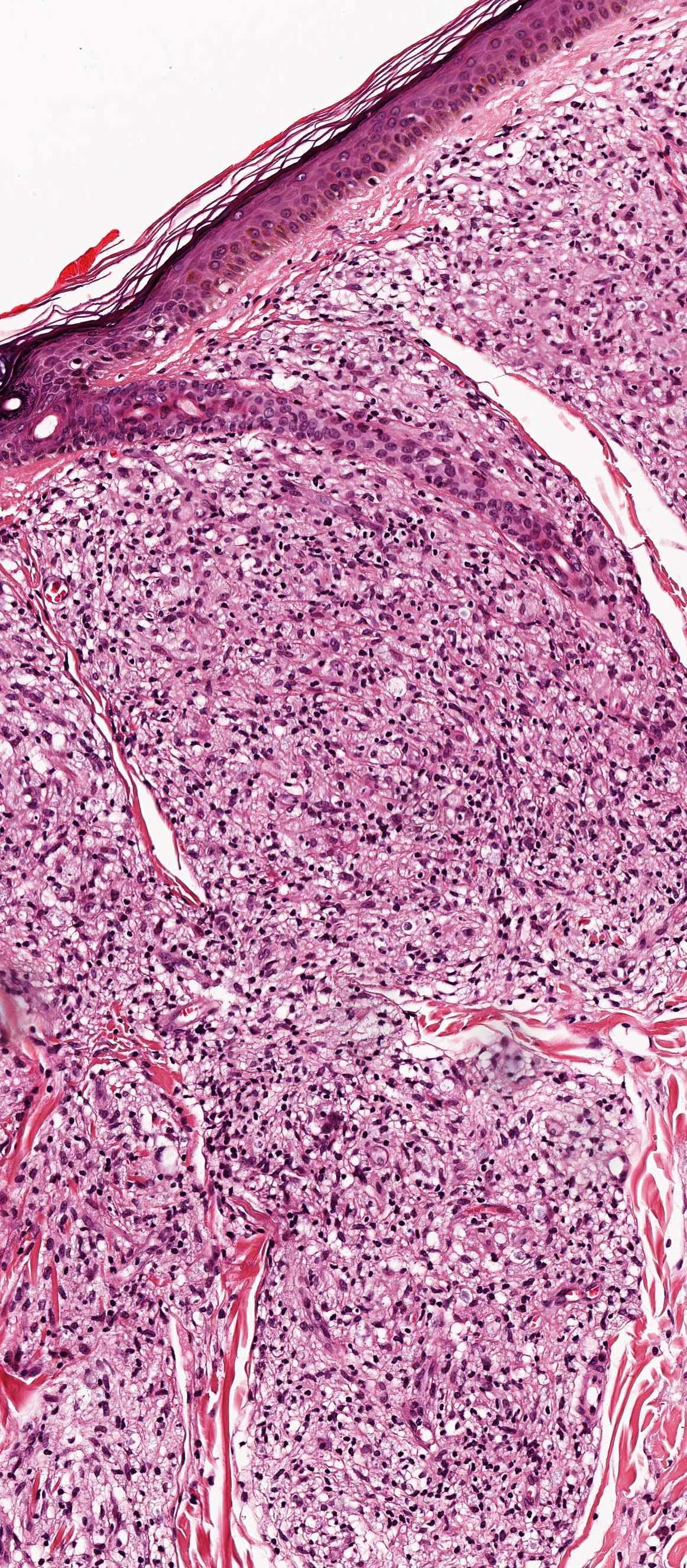
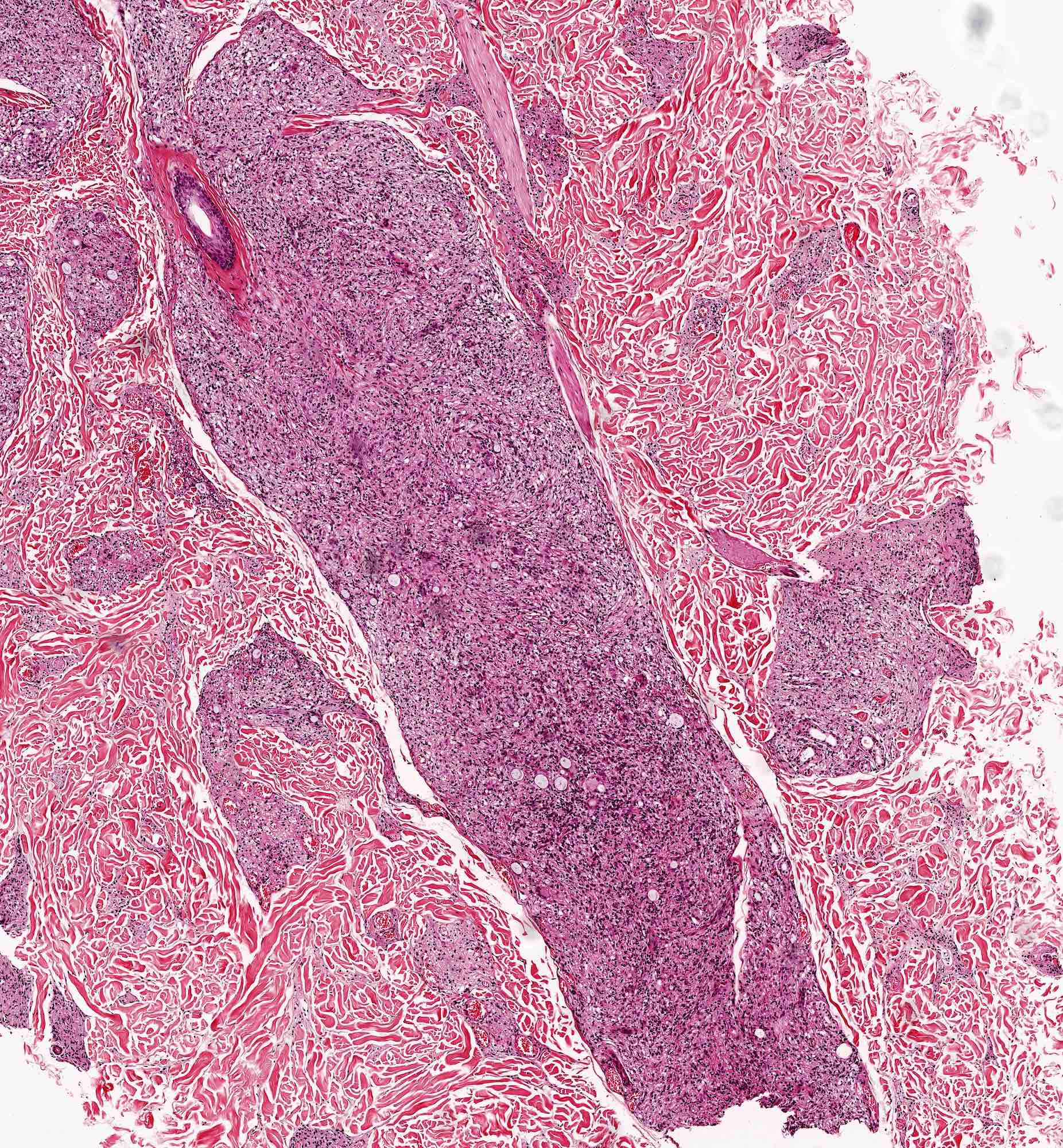
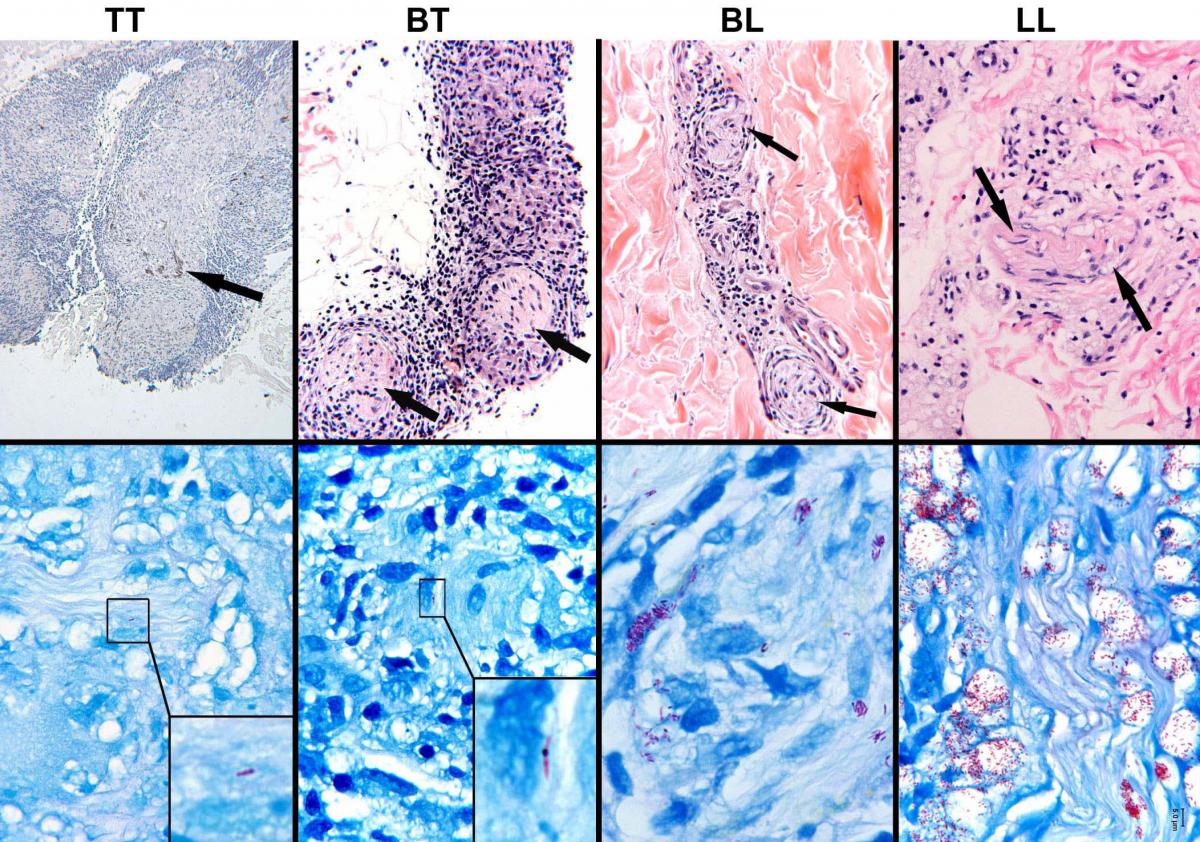
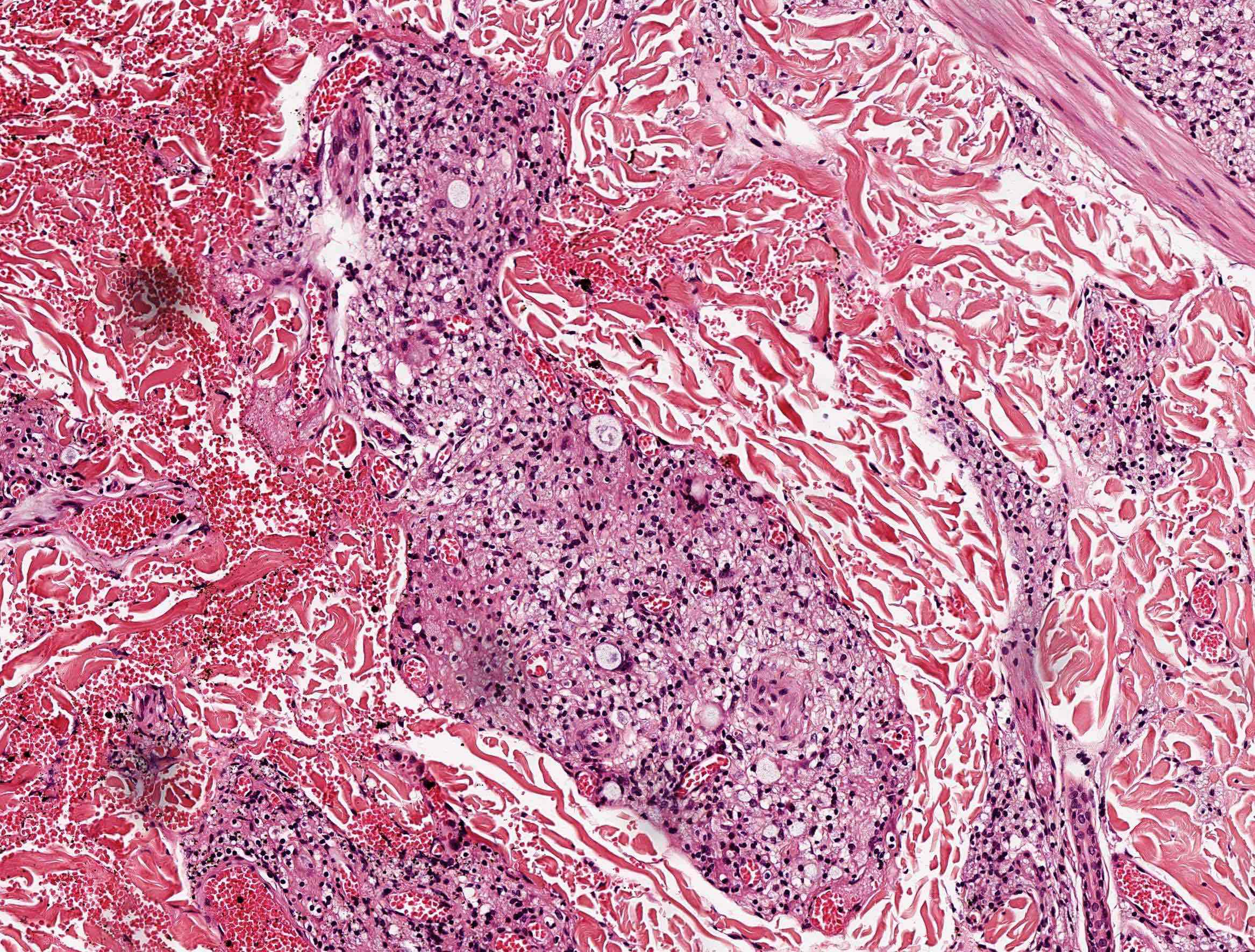
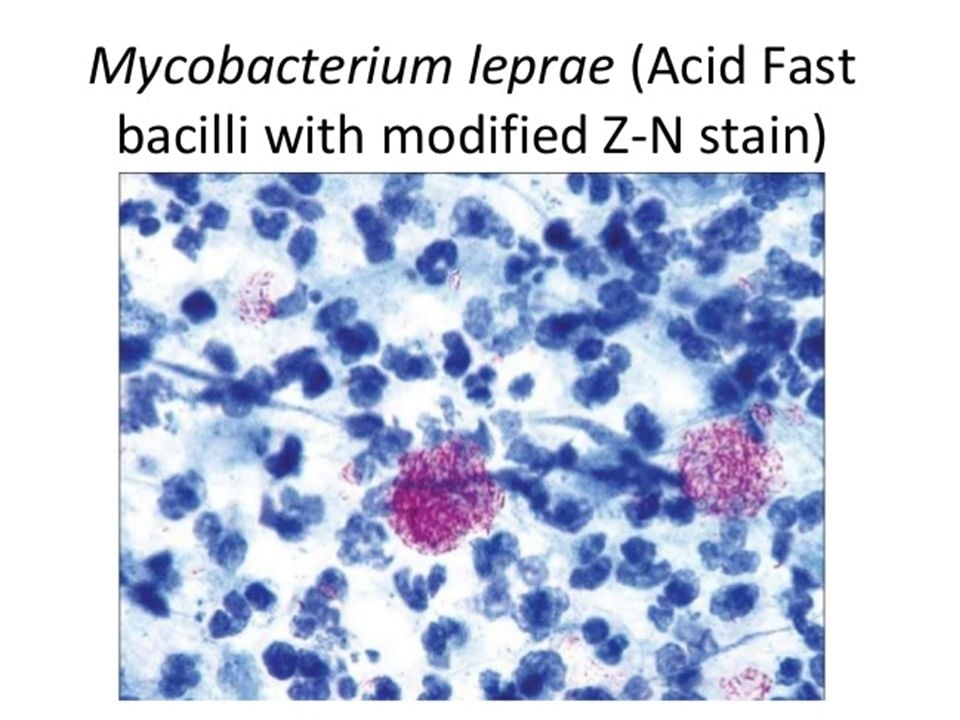
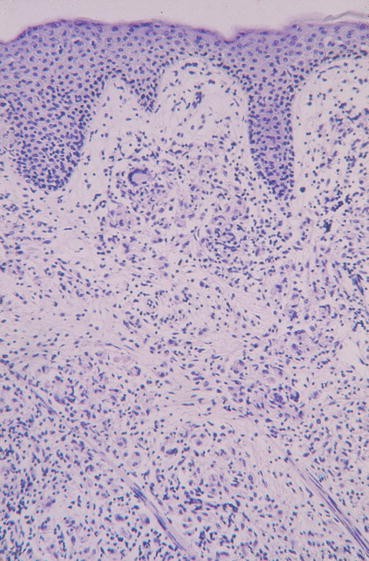
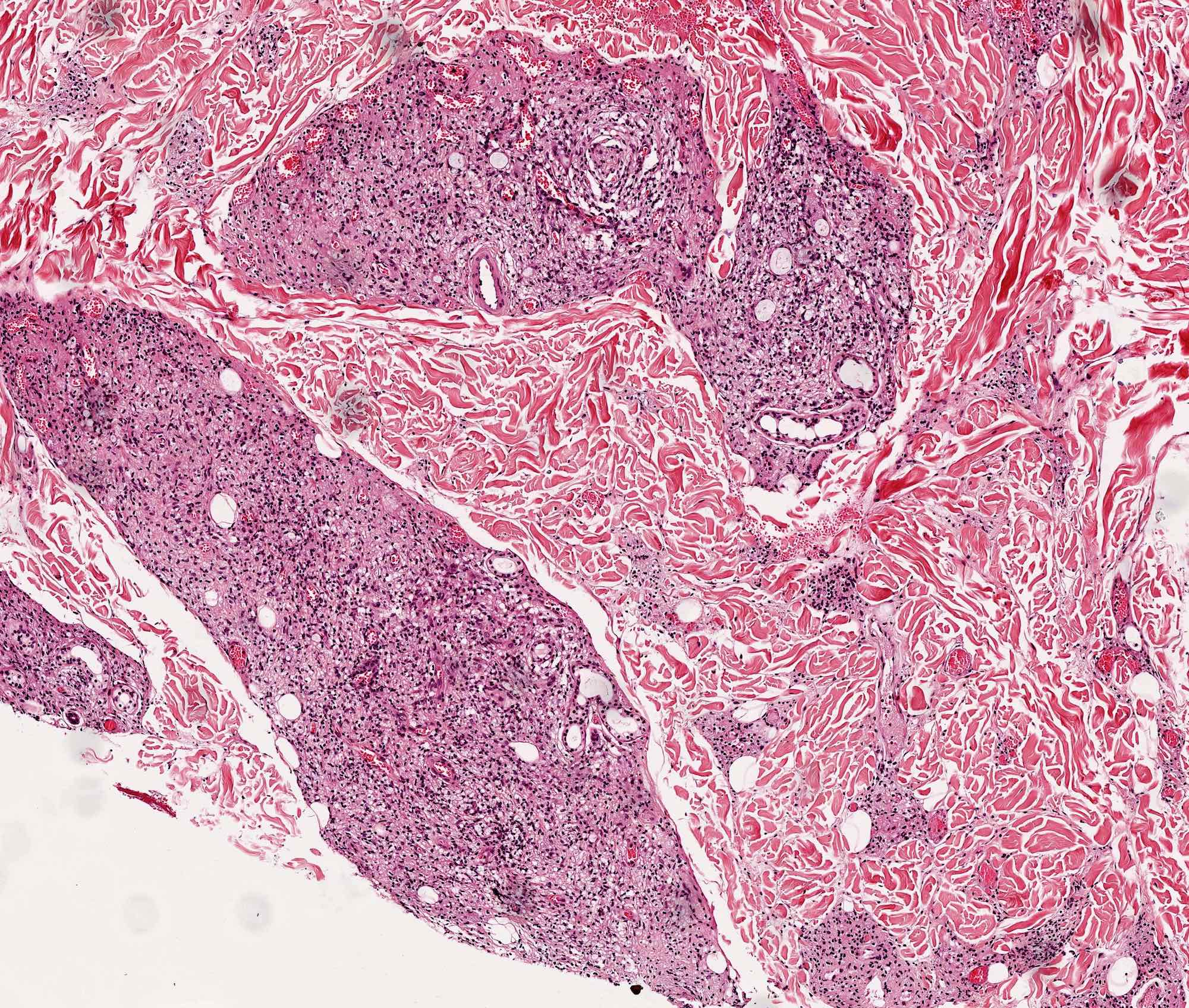
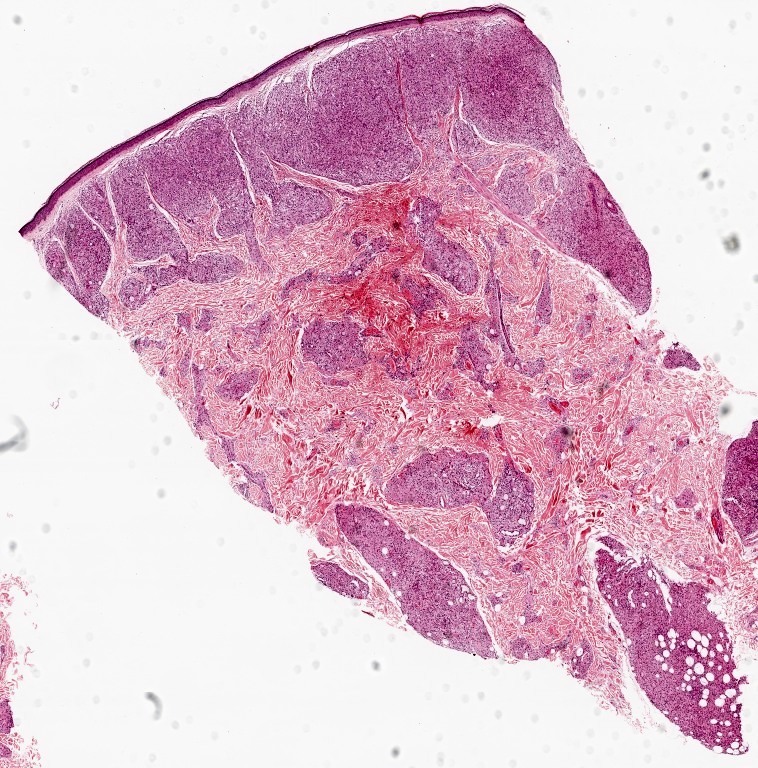
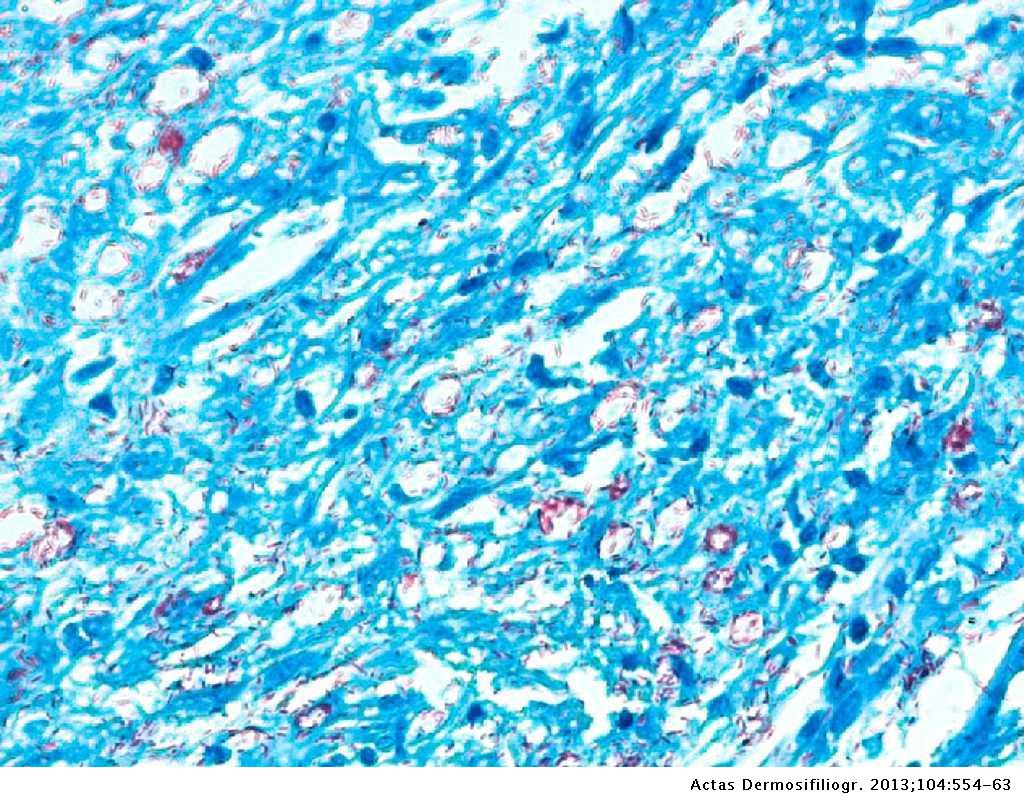
Lepra cells definition. Lepra cells lepra cells distinctive large mononuclear phagocytes macrophages with a foamlike cytoplasm and also poorly staining saclike structures resulting from degeneration of such cells observed characteristically in leprous inflammatory reactions. It is a strongly acid fast rod shaped organism with parallel sides and rounded ends. Medical definition of lepra cells.
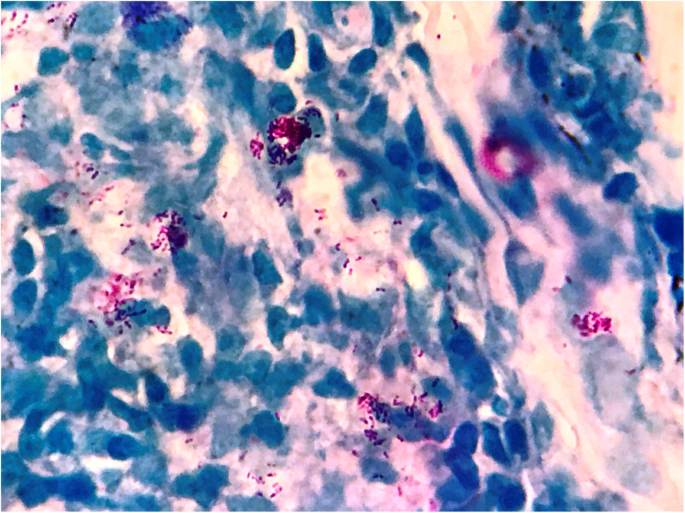
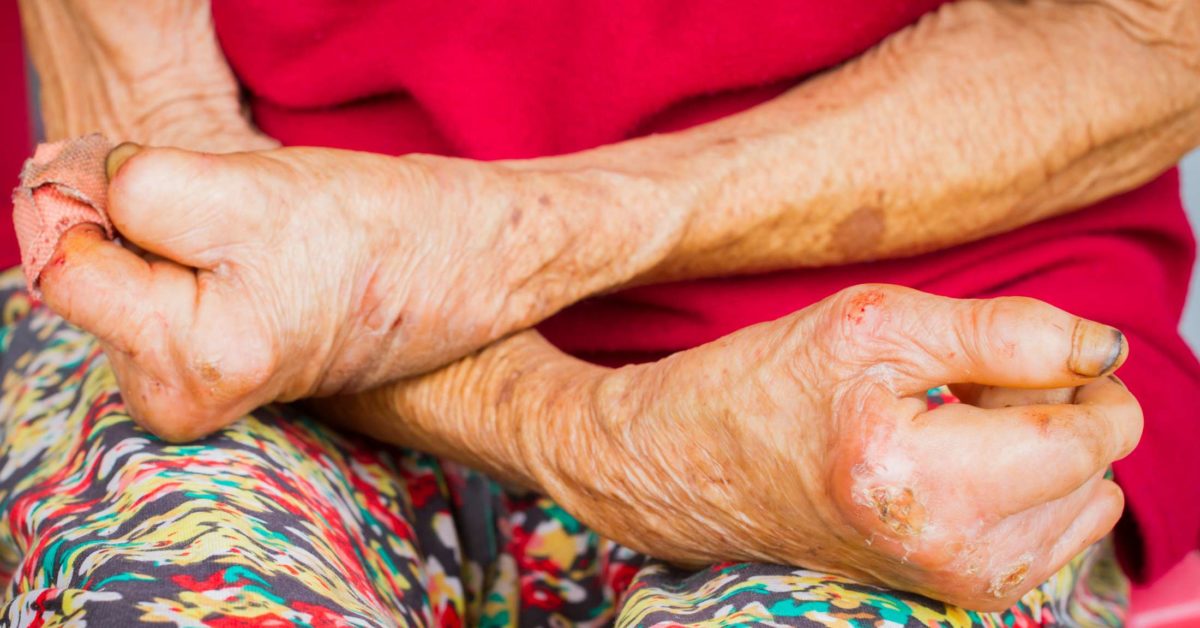
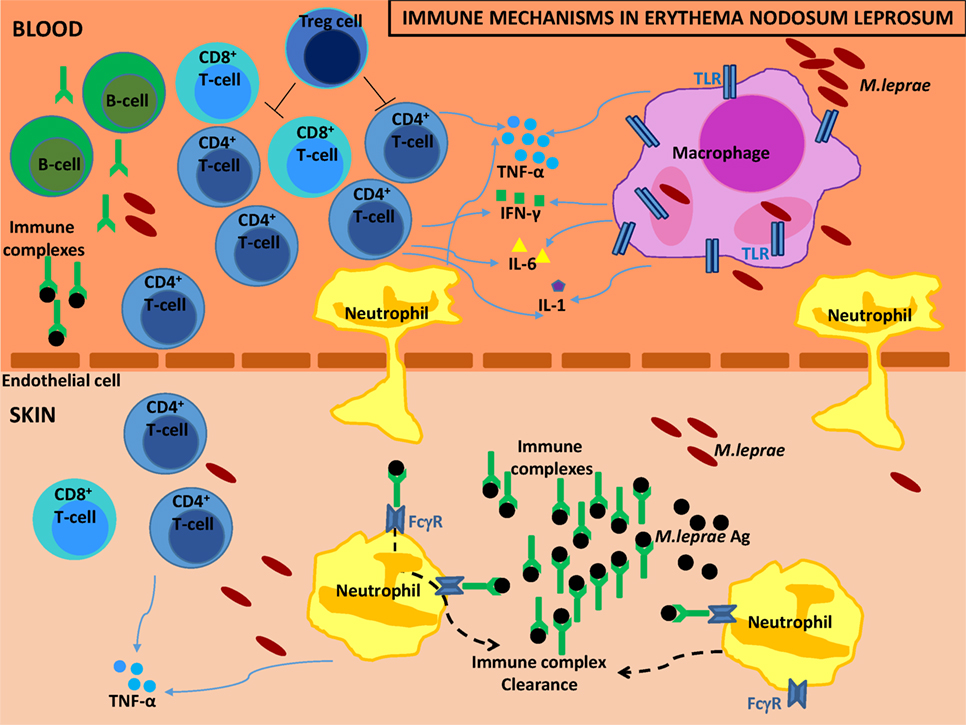
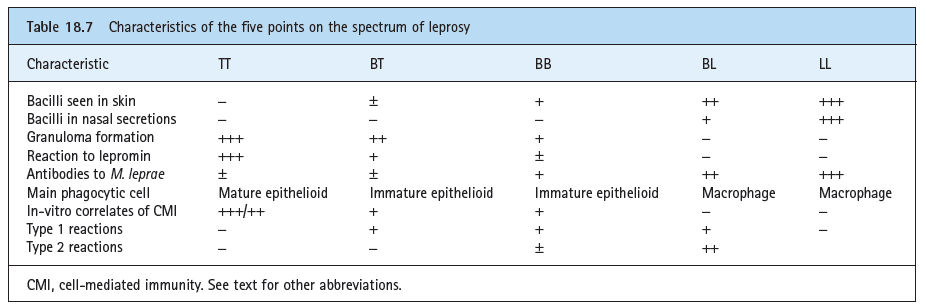
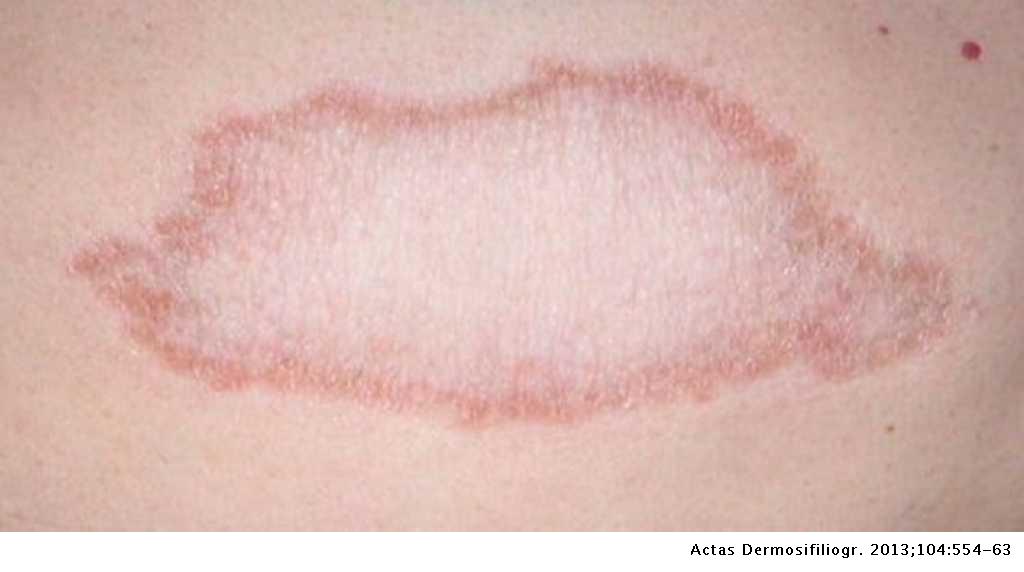
Lepro se an inflammatory disease caused by mycobacterium leprae manifested in various ways depending on the hosts ability to develop cell mediated immunity. Indistinct staining results from numerous fairly closely packed leprosy bacilli which are acid fast and resistant to staining by ordinary methods but may be vividly demonstrated by acid fast staining procedures. Indistinct staining results from numerous fairly closely packed leprosy bacilli which are acid fast and resistant to staining by ordinary methods.
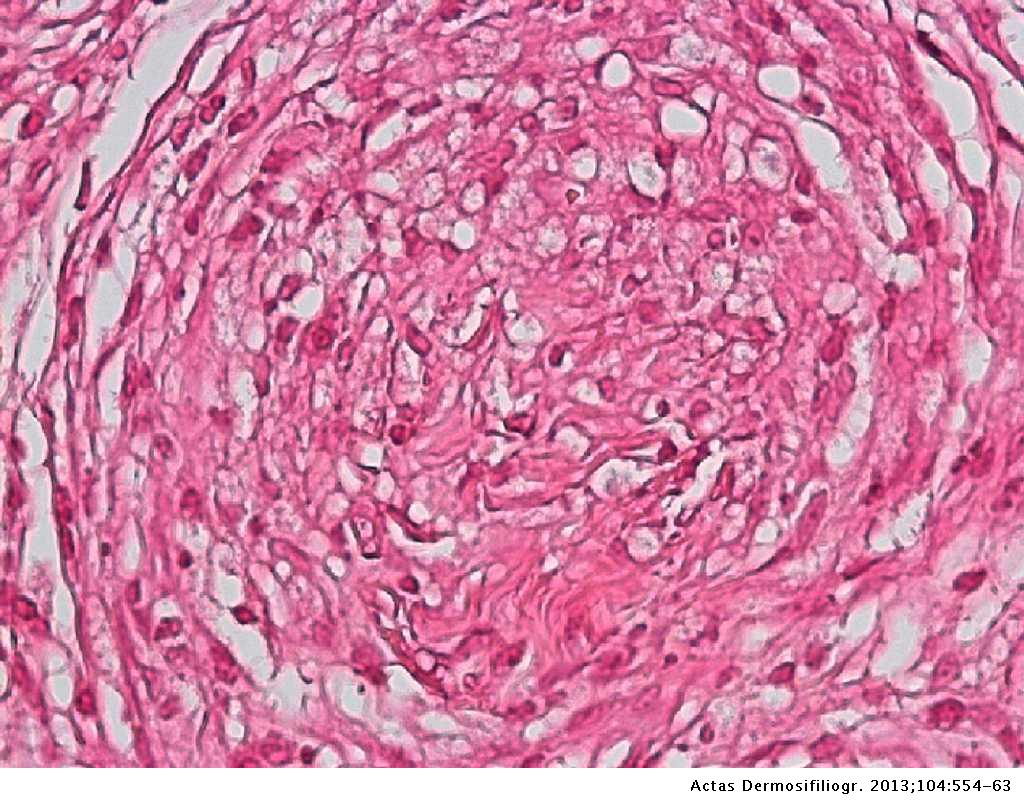
Distinctive large mononuclear phagocytes macrophages with a foamlike cytoplasm and also poorly staining saclike structures resulting from degeneration of such cells observed characteristically in leprous inflammatory reactions. It occurs in large numbers in the lesions of lepromatous leprosy chiefly in masses within the lepra cells often grouped together like bundles of cigars or arranged in a palisade. There it is able to withstand the onslaught of enzymes and other forces by virtue of possessing a peculiarly resistant waxy coat and thanks also to its association with lowered cellular immunity.
The bacillus responsible for leprosy hansen disease.